Introduction
Introduction

This chapter provides an overview of MARS ADVANTAGE functionality and provides a processing overview necessary for understanding how MARS ADVANTAGE works. This chapter also summarizes management responsibilities for MARS ADVANTAGE.
This chapter covers the following topics:
MARS ADVANTAGE is a complete financial management system specifically designed to support the functions performed by local governments, state governments, school districts, and higher education institutions. In addition to the standard accounting functions of accounts payable, accounts receivable and general ledger, MARS ADVANTAGE also performs the specialized functions of encumbrance control, fund accounting, grants, and project management. Using data provided by users, MARS ADVANTAGE maintains a financial database that can be used to produce a variety of detail and summary level reports.
Because significant differences exist between effective financial management in the public and private sectors, MARS ADVANTAGE is designed specifically to meet the financial information needs of the public sector. The result is a system that provides comprehensive, efficient, site-specific functionality and easy, straightforward use.
MARS ADVANTAGE provides real-time processing, system integration, host-workstation links, and a comprehensive decision-support tool. The system is powerful enough to meet your expanding information needs, yet uncomplicated enough for your non-technical personnel to use easily.
Full Integration of Financial Data
MARS ADVANTAGE architecture provides complete functional and technical integration across all modules. It allows comprehensive front-end editing and maintenance of a single, unified database. It also updates all database records simultaneously and uses a single account structure. This provides users across your organization with a consistent view of the system, and allows them to operate from the same base of information. The consistency and accuracy of financial information is assured.
The benefits of this approach are substantial:
- Integrated processing provides consistent management information.
- Single data entry reduces clerical burden.
- No back-end interfaces reduces operations costs and risks.
- Single-event processing improves auditability and lowers audit costs.
The figure which follows illustrates the integration of various base financial system components.
System control windows in MARS ADVANTAGE let you select the features and options that are appropriate for your organization without requiring software modifications to the basic system.
With MARS ADVANTAGE, you select the set of options and procedures that best meet your requirements. For example, you may elect to budget by organization in certain funds but use activity budgets in other special funds. You can also vary the levels where you want to exercise budgetary control.
Comprehensive Decision Support
MARS ADVANTAGE combines a complete set of reporting and inquiry capabilities with an integrated, unified database. This gives your users total access to financial information. Effective, timely reporting requires your system to be easily used by business, departmental, and data processing staffs. The ideal systems must support both common and unusual inquiry needs using all the processing benefits available within the host-workstation environment. In addition, it must meet these needs while ensuring the consistency and accuracy of your data.
MARS ADVANTAGE approach provides a total decision support environment based on the need for easy access to all your financial information.
This environment is designed so that it can be tailored to your unique needs. Decision support tools available with MARS ADVANTAGE include:
- Online Inquiry. More that 120 structured online views of the integrated database, designed to answer routine questions about your financial data.
- Standard Reports. Over 100 standard reports that cover management and financial reporting needs.
- ADVANTAGE/DS. Tailored to MARS ADVANTAGE for downloading data and reformatting for use with PC-based data analysis packages (uploads under full edits).
- Report Distribution. A product that automates the distribution of your routine reports by defining which reports go to specific users and assembling them into standard packets.
With MARS ADVANTAGE, each of these facilities accesses all information in the system. No artificial boundaries or borders between modules are crossed. Each facility uses the Report Data Dictionary to ensure consistency across applications. Check with your System Administrator for the tools that are available at your installation.
MARS ADVANTAGE is designed to provide fund-based financial accounting, Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) based reporting, and integrated encumbrance and budgetary control.
Automated Accounting for Funds
MARS ADVANTAGE provides automated accounting for all fund types necessary to support accounting. You can define as many individual funds as needed to effectively account for your operation both in terms of local legislation and GAAP-based financial reporting. MARS ADVANTAGE ensures that debits equal credits within each fund, and edits to control the types of transactions that are posted to a particular fund.
Based on the fund type, these entries are properly classified for both financial reporting and budgetary control. Support for all fund types automates CAFR Reporting. See The Chart of Accounts for a listing of the fund types supported by MARS ADVANTAGE.
In order to meet both generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) and local reporting requirements, the accounting system for many users must be capable of reporting its results on different bases of accounting. GAAP currently specifies that entities report on either the full or modified accrual basis, depending upon fund type. The most recent Government Accounting Standards Board (GASB) exposure draft recommends a move to accrual accounting for all funds to more accurately reflect inter-period equity. However, compliance with local legislation, particularly in terms of budgetary reporting, may require you to report on a cash basis.
MARS ADVANTAGE permits simultaneous reporting on all accounting bases by proper classification of accounting events at the transaction level. The reporting processes simply select the appropriate records based on the requirements for a report. Complex, manual calculations are not necessary to get from one accounting basis to the other.
One of the key characteristics of public sector accounting is the close relationship between budget and operational accounting. An entity reports the results of operations in terms of financial position. It also reports performance against the officially adopted budget. MARS ADVANTAGE meets this need by integrating budgetary accounting and budget controls with financial accounting.
MARS ADVANTAGE generates, and posts to the accounting system, entries to record both the appropriations and estimated revenues for the entity. Processing budgetary entries continues throughout the fiscal year; handling transfers, modifications, reversions, and lapses or carryovers at year-end.
In addition to formal accounting for budgetary transactions, many significant accounting events differentiate public sector accounting from the private sector. These include:
- Accounting for encumbrances, with the associated reservation of fund balance.
- Distinguishing between expenditures (for budgetary control) and expenses (for financial reporting) in certain fund types.
- Multiple types of transactions between funds (quasi-external purchase/sale, expense reimbursement, operating transfers, and residual equity transfers).
- Separate treatment of general fixed assets and long term debt.
- Specialized accounting when warrants are used to handle disbursements.
MARS ADVANTAGE provides specialized transactions, using table-driven processing, to handle each of these accounting events. This ensures that your general ledger and appropriate sub-ledgers accurately record all the various types of accounting events and properly classify them for reporting.
Specialized transactions to handle accounting events are standard features. The following illustration lists some of the specific processing handled by MARS ADVANTAGE.
Flexible Account Classification
MARS ADVANTAGE permits users to classify, record, and report on financial information based on the specific organization's system codes. MARS ADVANTAGE enables the reporting on those codes so all planning, budget control, financial management, and external reporting needs are simultaneously addressed.
The following financial transactions are available within MARS ADVANTAGE:
- Encumbrances, with associated reservation of fund balance
- Optional pre-encumbrances
- Automated liquidation of encumbrances and pre-encumbrances
- Expenditure not expense for capital acquisitions
- Internal accounting
- Quasi-external purchase/sale
- Expense reimbursement
- Operating transfer
- Residual equity transfer
- Fixed asset accounting
- Acquisition
- Depreciation
- Transfer
- Betterment
- Internal sale
- External sale
- Warrant accounting
- In operating fund
- Registered warrants
- In warrant clearing fund
- Budgetary accounting
- Appropriations
- Estimated revenues
- Allotments
You Design Your Own Chart of Accounts
MARS ADVANTAGE gives you the flexibility of defining a custom coding structure; one that produces a flexible set of financial reports where the same dollar amounts are classified differently. Program managers can get activity reports that cut across organizational lines. Line managers receive organization reports; decision-makers receive appropriation reports. All report types are produced from the same, unified database.
When MARS ADVANTAGE is initially installed, the coding structure is defined to meet organization specified requirements. Any codes not initially used are available as requirements change. Additionally, unused codes are blank, and zero filling is not required.
Each Area of Classification is Uniquely Identified
If an entity has to report on each of the dimensions needed to support its various constituencies, a flexible but standardized structure must be provided. MARS ADVANTAGE provides an account structure which classifies financial information according to each of the dimensions needed to support the various uses of financial information. This allows categorization of each transaction recorded by as many, or few, of these independent characteristics as necessary. The following presents a few examples of the MARS ADVANTAGE account classification structure
|
Object of Expenditure/Sub-Object of Expenditure, Revenue Source/Sub-Revenue Source, Balance Sheet Account |
|
MARS ADVANTAGE furnishes the following three codes to define what is typically called an account:
- The Object of Expenditure code classifies each expenditure according to the item or service purchased.
- The Revenue Source code designates the type of revenue or the source of the funds.
- The Balance Sheet Account code identifies the specific balance sheet account to be posted.
System Tables Reduce Coding and Provide Reporting Inferences
MARS ADVANTAGE takes advantage of system tables to minimize actual coding requirements. This is accomplished in two ways.
- When a direct relationship between codes exists, MARS ADVANTAGE infers one code from the other. For example, Activity and Function are inferred from Organization; Grant is inferred from Organization or Activity; Project is inferred from Job Code, etc.
- MARS ADVANTAGE uses individual reference tables to define hierarchical relationships that may exist within a coding classification dimension. For example, the object (office supplies) is related to an object class (supplies) within an object category.
Rather than force you to fit these definitions into the values you assign to the Object code (and limiting the number of hierarchical groupings you can use), or explicitly coding them and expanding the number of digits to be coded, MARS ADVANTAGE infers these higher level codes for reporting from reference tables. Because these fields are only used for reporting, they are inferred at reporting time. This reduces storage requirements.
Availability of funds is checked at transaction entry. Authoritative accounting standards dictate that the accounting system should provide the basis for budgetary controls. MARS ADVANTAGE integrates budget with accounting to verify that no procurement transaction exceeds available authority at the designated control levels. Therefore, all spending (requisitions, pre-encumbrances, encumbrances, and expenditures) are checked against the appropriate budget balances in a real-time environment.
If the transaction exceeds the available balance, it is rejected and the system displays an insufficient funds error message. Budget modifications are processed to make funds available. If the transaction is accepted, the spending amounts and available balances are immediately updated. This provides managers with a timely, accurate, and consistent view of their financial position.
Flexibility in Defining Control Levels
MARS ADVANTAGE lets you define spending controls at the levels of your organization that meet your requirements. You can establish budgets for:
With this flexibility, you can establish detailed or summary-level controls. Each control can be set and exercised independently and varied across funds. Further, you can code transactions at more detailed levels than those where you exercise budgetary controls. You can control by appropriations in the General Fund, by activity in Special Revenue funds, and by organization in Enterprise Funds.
Additional Capabilities Handle Special Situations
Certain entities, or certain components of entity operations, may be subject to specialized control requirements. These include time-phased controls of amounts for less than a year; multi-year authority for continuing appropriations that span multiple fiscal years; revolving fund accounts where controls are based upon cash actually received; or grant and reimbursable activities with multiple funding sources where the ceiling includes a local component and an estimated reimbursement amount from outside sources.
MARS ADVANTAGE provides the following additional control features and options to accommodate these types of situations. These features are outlined below.
These capabilities are available as needed to handle unique control requirements.
MARS ADVANTAGE employs a table-driven security mechanism that allows users to perform functions at various security levels, from system administration to inquiry and reporting. See MARS ADVANTAGE Security for more information on system security options.
The financial system of an entity must meet the reporting needs of many different audiences. These may include the legislature, the financial community, local citizens, grantor agencies, regulatory bodies, and internal managers. The needs of each of these groups vary significantly.
MARS ADVANTAGE provides standard reports that address basic accounting, financial management, and external reporting requirements rather than requiring you to develop these reports at your site. These include standard Comprehensive Annual Financial Reports (CAFR) and supporting schedules that meet GAAFR, GASB, NACUBO, and FASB reporting requirements. MARS ADVANTAGE also includes tools that let you develop any other reports required.
In addition to MARS ADVANTAGE standard CAFR reporting capabilities, there is an interface between MARS ADVANTAGE and the Government Financial Officers Association's (GFOA) CAFRonMICRO?. CAFRonMICRO? is a PC-based application designed to provide CAFR reporting that meets the rigorous guidelines of the GFOA's Certificate of Achievement for Excellence in Financial Reporting. The interface enables data to be imported to CAFRonMICRO?. The software can then be used for comprehensive CAFR reporting and for preparing financial statements on a basis other than GAAP.
Security in MARS ADVANTAGE is enforced through a collection of system tables and their corresponding windows. A brief discussion of each follows. For more information, see the Security and Approval Functions manual.
Security restrictions are primarily enforced through the user ID defined in Security (STAB). In addition to the user ID, an Agency code must be entered on the Document Listing (SUSF) prior to data entry. The security profile associated with the user ID determines which Agency codes are valid. MARS ADVANTAGE also provides the option to enforce security at the organization level. If this option is chosen, a valid Organization code must be entered on the Document Listing (SUSF).
The Agency (SEC1) and Organization (SEC2) codes can also be used to enforce line level security. For example, if users are only authorized for agency 470 and line level security is chosen, they must enter 470 on the Document Listing (SUSF) and are then restricted to entering line data that only affects agency 470.
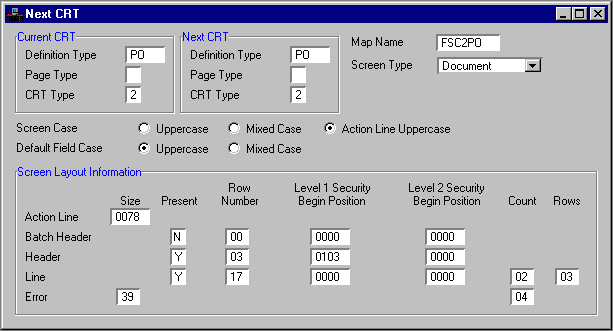
The following paragraph describes updating Format Definition for Tables (FOR2) and Next CRT (NCRT) online. You can update these tables manually, or they can also be updated offline by your system administrator using the CRT Generation (CRTGEN) program.
Line level security can be defined at either the document header (DOCH) or the document detail (DOCD) level. However, Level 1 Security (SEC1) and Level 2 Security (SEC2) codes cannot be defined in both the header and the detail lines. Therefore, if the Level 1 Security (SEC1) code is defined in the header, the Level 2 Security (SEC2) code must also be defined in the header.
To activate line level security, the Level 1 Security (SEC1) offset position (agency) must be entered in either the Level 1 Security Begin Position Header field or the Level 1 Security Begin Position Line field in Format Definition for Tables (FOR2) and Next CRT (NCRT). If this value is defined in the Level 1 Security Begin Position Header field, header level security is established. If this value is defined in the Level 1 Security Begin Position Line field, document detail security is established. To determine the offset position of the Level 1 Security (SEC1) code, search the document's COBOL layout for the DOCH code, locate the Level 1 Security (SEC1) code, and calculate the offset position.
If the Level 1 Security code is not found in DOCH, search for the DOCD code. Locate the Level 1 Security code and enter the offset position in the Level 1 Security Begin Position Line field. Next CRT (NCRT) has multiple records for each document; each record must be updated with the Level 1 Security offset position before line level security can be enforced.
If your installation enforces security at the Level 2 Security (SEC2) (organization) level, the offset position of the Level 2 Security (SEC2) code must be entered in either the Level 2 Security Begin Position or Level 2 Security Begin Position Line field.
To derive the offset position of a header element from the COBOL layout, follow the steps below:
- Locate the DOCH code in the COBOL layout.
- Locate the Level 1 Security code. The Level 1 Security code in the example that follows is HDR-AGCY.
- Starting at DOCH (offset=0), add element PIC X values to determine the offset position of the Level 1 Security code. The Level 1 Security offset position is derived as follows: TRANS-CODE starts at 1 and is 2 characters long, therefore the offset value of TRANS-NUMBER is 3. TRANS-NUMBER starts at 3 and is 11 characters long, therefore the offset value of HDR-AGCY is 14.
- Substitute DOCD for DOCH to derive the offset position of elements in the document detail section.
Sample entries for the Format Definition for Tables (FOR2) and Next CRT (NCRT) windows are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, respectively. These entries establish document header security at both the Level 1 Security (SEC1) (agency) and SEC2 (organization) levels. The values in the Level 1 Security Begin Position Line and Level 2 Security Begin Position Line fields on both Format Definition for Tables (FOR2) and Next CRT (NCRT) correspond to the offset positions derived from the COBOL layout. Since Next CRT (NCRT) has multiple records for each document, refer to the Next CRT Type field to ensure that all records are updated.
Format Definition for Tables (2 of 2) (FOR2)